判断题 (1)递归程序往往简洁易懂,但占用较大空间。递归层数过大会造成系统堆栈溢出。
(2)图是表示多对多关系的数据结构。
(3)Depth First Search on a graph uses Stack structure for its implementation.
(4)只有当局部最优跟全局最优解一致的时候,贪心法才能给出正确的解。
(5)令S为活动选择问题(Activity Selection Problem)中所有活动的集合。则一定存在S的某个最大相容活动子集是包含了最早结束的活动a
(6)哈夫曼编码是一种最优的前缀码。对一个给定的字符集及其字符频率,其哈夫曼编码不一定是唯一的,但是每个字
符的哈夫曼码的长度 一定是唯一的。
单选题 若某线性表最常用的操作是在表尾进行插入和删除,则利用哪种存储方式最合适?
数组
下列对顺序存储的有序表(长度为 n )实现给定操作的算法中,平均时间复杂度为 O (1) 的是:
获取第 i (1≤i ≤n )个元素的算法
线性表L=(a1, a2 ,……,a100 )用一维数组存储。删除线性表中的元素a50,需要移动元素的个数是( )。
50
顺序表中第1个元素的存储地址是2000,每个元素的长度为4,则第5个元素的地址是( )
2016
To run binary search in a sorted sequencial list of 600 elements, the maximum number of comparisons is:
10
设 0≤i ,k <n ,下面这段代码的时间复杂度是:
if (i>k) { for (j=i; j<n; j++) a[j] = a[j-k]+1; } else { for (j=i; j>0; j--) a[j] = a[k-j]+2; }
O(n)
下列程序段的时间复杂度是
int sum = 0; for(int i=1;i<n;i*=2) for(int j=0;j<i;j++) sum++;
O(n)
快速排序算法是根据( )思想设计的算法。
分治算法
()关于分治法描述不正确 的是:
随机生成100个整数并存放在一个数组中,然后从中指定一个整数,则可用二分搜索算法在O (lo g**n )的时间内找到该整数。
具有n个结点的图,为了存储结点对之间的关系,可采用( )大小的矩阵。
n * n
一个有n个顶点的简单有向图最多有 ( ) 条边
n * (n - 1)
图的广度优先遍历需要借助的数据结构是
队列
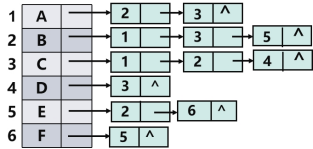
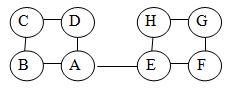
已知图的邻接表如下图所示,则从顶点A出发按广度优先遍历的结果是( )。
ABCEDF
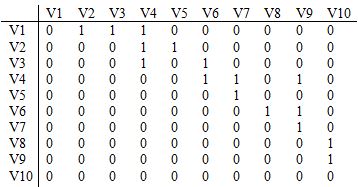
给定一个图的邻接矩阵如下,则从V1出发的宽度优先遍历序列(BFS,有多种选择时小标号优先)是:
V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6, V7, V9, V8, V10
以下算法的功能是()。
void graph1( adjmatrix GA, int i, int n, int *visited) { int k, j; Queue q; cout<<i<<‘ ‘; visited[i]= 1; InitQueue( q); EnQueue (q, i); while ( !EmptyQueue(q) ) { k= OutQueue (q); for( j=0; j<n; j++) { if ( GA[k][j] != 0 && GA[k][j] != MaxValue && !visited[j] ) { cout<<j<<‘ ‘; visited[j] = 1; EnQueue (q, j); } } } }
从顶点 i 出发进行广度优先遍历
图的广度优先遍历类似于二叉树的:
层次遍历
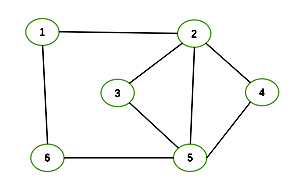
在图中自c点开始进行广度优先遍历算法可能得到的结果为:
c,f,a,d,e,b
对下图从顶点C出发进行深度优先搜索,哪个是错误的搜索序列?
CDABEHFG
The following graph has Euler circuits. If the depth-first search is used to find an Euler circuit by concatenating paths, which sequence of the following is incorrect?
5,3,5,4,2,5,6,1,5
图的深度优先遍历类似于二叉树的:
先序遍历
下列说法不正确的是:
图的深度遍历不适用于有向图
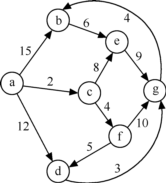
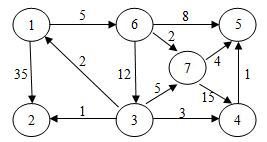
有向网如图所示,试用迪杰斯特拉算法求出从顶点a到其他各顶点间的最短路径,各顶点依次被确定的顺序为( )
a,c,f,e,d,g,b
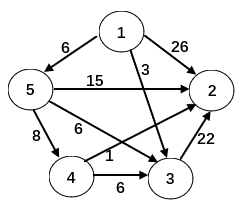
使用 Dijkstra 算法求下图中从顶点 1 到其余各顶点的最短路径,将当前找到的从顶点 1 到顶点 2、3、4、5 的最短路径长度保存在数组 dist 中,求出第二条最短路径后,dist 中的内容更新为:
21、3、14、6
使用迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法求下图中从顶点1到其他各顶点的最短路径,依次得到的各最短路径的目标顶点是:
6, 7, 5, 3, 2, 4
数据结构中Dijkstra算法用来解决哪个问题?
最短路径
我们用一个有向图来表示航空公司所有航班的航线。下列哪种算法最适合解决找给定两城市间最经济的飞行路线问题?
Dijkstra算法
函数题 递归实现指数函数 #include <math.h> double calc_pow ( double x, int n ) { double fact=1 ; int i; if (n==0 ){ return 1 ; }else if (n==1 ){ return x; }else { calc_pow(x, n-1 );c fact=pow (x, n); return fact; } }
递归计算P函数 double P ( int n, double x ) { if (n<=0 ){ return 1 ; }else if (n==1 ){ return x; }else { return ((2 *n-1 )*P(n-1 ,x)-(n-1 )*P(n-2 ,x))/n;c } }
邻接表存储图的广度优先遍历 void BFS ( LGraph Graph, Vertex S, void (*Visit)(Vertex) ) { Visit(S); Visited[S] = true ; Vertex queue [105 ]; int front = 0 , rear = 0 ; queue [rear++] = S; PtrToAdjVNode p; while (front < rear){ Vertex x = queue [front++]; p = Graph->G[x].FirstEdge; while (p){ Vertex v = p->AdjV; if (!Visited[v]){ Visit(v); Visited[v] = true ; queue [rear++] = v; } p = p->Next; } } }
编程题 猜数字-交互版 import java.io.*;import java.math.*;import java.util.*;public class Main { static InputReader ir = new InputReader (System.in); static Read in = new Read (); static Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (System.out))); public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException{ int T = 1 ; while (T-- > 0 ) solve(); out.flush(); } public static void solve () throws IOException{ int n = ir.nextInt(); int l = 1 , r = n; while (l <= r) { int mid = l + r >> 1 ; out.println(mid); out.flush(); String s = ir.next(); if (s.equals("<" )) { r = mid - 1 ; }else { l = mid + 1 ; } } out.println("! " + r); out.flush();; } } class InputReader { private final static int buf_size = 65536 ; BufferedReader br; StringTokenizer st; public InputReader (InputStream in) { br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (in), buf_size); st = new StringTokenizer ("" ); } public String next () throws IOException { while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) { st = new StringTokenizer (br.readLine()); } return st.nextToken(); } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ return Integer.parseInt(next()); } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ return Double.parseDouble(next()); } public long nextLong () throws IOException{ return Long.parseLong(next()); } } class Read { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer (br); int s; public String next () throws IOException { s = st.nextToken(); return st.sval; } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return (int ) st.nval; } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return st.nval; } }
两个有序序列的中位数 #include "stdio.h" #include "math.h" #define N 100000 int main () { int a[N],b[N],c[2 *N]; int n,i,ai=0 ,bi=0 ; scanf ("%d" ,&n); for (i=0 ; i<n; i++) { scanf ("%d" ,&a[i]); } for (i=0 ; i<n; i++) { scanf ("%d" ,&b[i]); } for (i=0 ; i<2 *n; i++) { if (a[ai]<=b[bi]) { c[i]=a[ai]; ai++; } else { c[i]=b[bi]; bi++; } } printf ("%d\n" ,c[(2 *n-1 )/2 ]); }
数组循环左移 int main () { int n,m; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&m); int a[n]; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) { scanf ("%d" ,&a[i]); } for (int i =0 ;i<m%n;i++) { int p = a[0 ]; for (int j =1 ;j<n;j++) { a[j-1 ] = a[j]; } a[n-1 ] = p; } for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) { if (i == 0 ) printf ("%d" ,a[i]); else printf (" %d" ,a[i]); } return 0 ;}
Merging Linked Lists #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <unordered_map> using namespace std;int main () int head1, head2, n; scanf ("%d %d %d" , &head1, &head2, &n); unordered_map<int , pair<int , int >> list; vector<pair<int , int >> l1, l2, ans; int address, num, next; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i){ scanf ("%d %d %d" , &address, &num, &next); list[address].first = num; list[address].second = next; } int tmp = head1; while (tmp != -1 ){ l1.emplace_back (tmp, list[tmp].first); tmp = list[tmp].second; } tmp = head2; while (tmp != -1 ){ l2.emplace_back (tmp, list[tmp].first); tmp = list[tmp].second; } int len1 = l1.size (); int len2 = l2.size (); if (len1 > len2){ int pos1 = 0 , pos2 = len2 - 1 ; while (pos2 >= 0 ){ ans.push_back (l1[pos1++]); ans.push_back (l1[pos1++]); ans.push_back (l2[pos2--]); } while (pos1 < len1) ans.push_back (l1[pos1++]); } else { int pos2 = 0 , pos1 = len1 - 1 ; while (pos1 >= 0 ){ ans.push_back (l2[pos2++]); ans.push_back (l2[pos2++]); ans.push_back (l1[pos1--]); } while (pos2 < len2) ans.push_back (l2[pos2++]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < ans.size (); ++i){ if (i == ans.size () - 1 ) printf ("%05d %d -1\n" , ans[i].first, ans[i].second); else printf ("%05d %d %05d\n" , ans[i].first, ans[i].second, ans[i + 1 ].first); } return 0 ; }
统计工龄 #include <stdio.h> int main () { int i, age, N; scanf ("%d" , &N); int arr[51 ]; for (i = 0 ;i <= 50 ;i++) arr[i]=0 ; for (i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { scanf ("%d" , &age); arr[age] ++; } for (i = 0 ; i <= 50 ; i ++) { if (arr[i]) { printf ("%d:%d\n" , i, arr[i]); } } }
冒泡排序 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define N 100 int main () { int n,k,arr[N],i,j,t; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&k); for (i=0 ;i<n;i++) { scanf ("%d" ,&arr[i]); } for (j=0 ;j<k;j++) { for (i=0 ;i<n-1 ;i++) { if (arr[i]>arr[i+1 ]) { t=arr[i]; arr[i]=arr[i+1 ]; arr[i+1 ]=t; } } } for (i=0 ;i<n-1 ;i++) { printf ("%d " ,arr[i]); } printf ("%d" ,arr[n-1 ]); return 0 ; }
整数分解为若干项之和 #include <stdio.h> # define MAX_SIZE 100 int items[MAX_SIZE];int count; int N; void f (int remain_value, int start, int num) if (remain_value!=0 ) { for (int i=start; i<=remain_value; i++) { items[num] = i; f (remain_value-i, i, num+1 ); } }else { count++; printf ("%d=%d" ,N,items[0 ]); for (int j=1 ; j<num; j++){ printf ("+%d" ,items[j]); } if (count%4 ==0 ) printf ("\n" ); else if (count%4 !=0 &&items[0 ]!=N) printf (";" ); } } int main () count=0 ; scanf ("%d" , &N); f (N, 1 , 0 ); return 0 ; }
输出全排列 #include <stdio.h> int a[10 ]={0 };void arrange (int a[], int n, int m) { int i,j,num; if (m==n){ for (i=0 ;i<n;i++){ printf ("%d" ,a[i]); } printf ("\n" ); return ; } else { for (num=1 ;num<=n;num++){ for (j=0 ;j<m;j++) if (a[j]==num) break ; if (j==m){ a[m]=num; arrange(a, n, m+1 ); } }return ; } } int main () { int n; scanf ("%d" , &n); arrange(a, n, 0 ); return 0 ; }
哪两个点之间的距离最近 #include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std;int main () int n; cin>>n; double x[n+1 ]; double y[n+1 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ cin>>x[i]>>y[i]; } int d1; int d2; double _min=0x3f3f3f3f ; for (int i=0 ;i<n-1 ;i++){ for (int j=i+1 ;j<n;j++){ double t=sqrt ((x[i]-x[j])*(x[i]-x[j])+(y[i]-y[j])*(y[i]-y[j])); if (t <_min){ _min=t; d1=i; d2=j; } } } if ((x[d1]+y[d1])>(x[d2]+y[d2])){ int t=d1; d1=d2; d2=t; } printf ("(%.2lf,%.2lf),(%.2lf,%.2lf),miniDist=%.3lf" ,x[d1],y[d1],x[d2],y[d2],_min); }
士兵排列 #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define Max 10000 int Compare (const void * e1, const void * e2) { return (int )*((int *)e1) - (int )*((int *)e2); } int add (int a[], int n,int mid) { int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { sum += abs (a[i]-mid); } return sum; } int main () { int x[Max] = { 0 }, y[Max] = { 0 }; int n = 0 ; scanf ("%d" , &n); int i = 0 ; for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { scanf ("%d%d" , &x[i], &y[i]); } qsort(x, n, sizeof (x[0 ]), Compare); qsort(y, n, sizeof (y[0 ]), Compare); for (i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { x[i] = x[i] - i; } qsort(x, n, sizeof (x[0 ]), Compare); int Y_mid = y[n / 2 ], X_mid = x[n / 2 ]; int y_sum = 0 , x_sum = 0 ; y_sum = add(y, n, Y_mid); x_sum = add(x, n, X_mid); printf ("%d\n" , x_sum + y_sum); return 0 ; }
词频统计 import reimport collectionsimport syswords = "" .join([line for line in sys.stdin]) words = re.compile (r"\w+" , re.I).findall(words.lower().split('#' )[0 ]) words = [each.strip() for each in words] words = list (map (lambda each: each[0 :15 ] if len (each) > 15 else each, words)) counter = collections.Counter(words) rank = sorted (counter.items(), key=lambda each: (-each[1 ], each[0 ]), reverse=False ) print (len (rank)) for each in rank[0 :int (0.1 *len (rank))]: print ("{}:{}" .format (each[1 ], each[0 ]))
打印学生选课清单 #include <stdio.h> int main () { int i, age, N; scanf ("%d" , &N); int arr[51 ]; for (i = 0 ;i <= 50 ;i++) arr[i]=0 ; for (i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { scanf ("%d" , &age); arr[age] ++; } for (i = 0 ; i <= 50 ; i ++) { if (arr[i]) { printf ("%d:%d\n" , i, arr[i]); } } } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> typedef struct classList { int cid; struct classList * next ; }CL; typedef struct classTable { CL* head; CL* tail; int cnt; }CT; const int N=26 *26 *26 *10 +1 ;CT* st[26 *26 *26 *10 +1 ]; int hs (char s[]) { return (int )((s[3 ]-'0' )+(s[2 ]-'A' )*10 +(s[1 ]-'A' )*26 *10 +(s[0 ]-'A' )*26 *26 *10 ); } int main () { for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ CT* t=(CT*)malloc (sizeof (CT)); t->head=(CL*)malloc (sizeof (CL)); t->head->next=NULL ; t->cnt=0 ; t->tail=t->head; st[i]=t; } int n,k; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&k); for (int i=1 ;i<=k;i++){ int bn,stn; scanf ("%d%d" ,&bn,&stn); for (int j=0 ;j<stn;j++){ char sid[5 ]; scanf ("%s" ,sid); int id=hs(sid); CL* t=(CL*)malloc (sizeof (CL)); t->cid=bn; t->next=NULL ; st[id]->tail->next=t; st[id]->tail=st[id]->tail->next; (st[id]->cnt)++; } } for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ char sid[5 ]; scanf ("%s" ,sid); printf ("%s" ,sid); int id=hs(sid); printf (" %d" ,st[id]->cnt); CL* p=st[id]->head->next; int * bk=(int *)malloc (sizeof (int )*(k+1 )); for (int i=1 ;i<=k;i++){ bk[i]=0 ; } while (p){ bk[p->cid]=1 ; p=p->next; } for (int i=1 ;i<=k;i++){ if (bk[i]==1 ){ printf (" %d" ,i); } } free (bk); printf ("\n" ); } return 0 ; }
深入虎穴 import java.io.*;import java.math.*;import java.util.*;public class Main { static InputReader ir = new InputReader (System.in); static Read in = new Read (); static Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (System.out))); public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException{ int T = 1 ; while (T-- > 0 ) solve(); out.flush(); } public static void solve () throws IOException{ int n = in.nextInt(); List<Integer>[] g = new List [n + 1 ]; Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList <>()); int [] inDeg = new int [n + 1 ]; int x = -1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int k = in.nextInt(); for (int j = 0 ; j < k; j++) { x = in.nextInt(); g[i].add(x); inDeg[x]++; } } int s = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (inDeg[i] == 0 ) { s = i; break ; } } Queue<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque <>(); q.offer(s); while (!q.isEmpty()) { x = q.poll(); for (int y : g[x]) { q.offer(y); } } out.print(x); } } class SegmentTree { long [] tree; long [] tag; int N; public SegmentTree (int [] a, int n) { N = n; tree = new long [N << 2 ]; tag = new long [N << 2 ]; build(a, 1 , 1 , N); } public int ls (int p) { return p << 1 ; } public int rs (int p) { return p << 1 | 1 ; } public void build (int [] a, int p, int pl, int pr) { if (pl == pr) { tree[p] = a[pl - 1 ]; return ; } int mid = pl + pr >> 1 ; build(a, ls(p), pl, mid); build(a, rs(p), mid + 1 , pr); push_up(p); } public void addTag (int p, int pl, int pr, long val) { tree[p] = (pr - pl + 1 ) * val; tag[p] = val; } public void push_down (int p, int pl, int pr) { if (tag[p] != 0 ) { int mid = pl + pr >> 1 ; addTag(ls(p), pl, mid, tag[p]); addTag(rs(p), mid + 1 , pr, tag[p]); tag[p] = 0 ; } } public void push_up (int p) { tree[p] = tree[ls(p)] + tree[rs(p)]; } public void update (int p, int pl, int pr, int l, int r, long val) { if (l <= pl && pr <= r) { addTag(p, pl, pr, val); return ; } push_down(p, pl, pr); int mid = pl + pr >> 1 ; if (l <= mid) update(ls(p), pl, mid, l, r, val); if (mid < r) update(rs(p), mid + 1 , pr, l, r, val); push_up(p); } public long query (int p, int pl, int pr, int l, int r) { if (l <= pl && pr <= r) { return tree[p]; } push_down(p, pl, pr); int mid = pl + pr >> 1 ; long res = 0 ; if (l <= mid) res += query(ls(p), pl, mid, l, r); if (mid < r) res += query(rs(p), mid + 1 , pr, l, r); return res; } } class InputReader { private final static int buf_size = 65536 ; BufferedReader br; StringTokenizer st; public InputReader (InputStream in) { br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (in), buf_size); st = new StringTokenizer ("" ); } public String next () throws IOException { while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) { st = new StringTokenizer (br.readLine()); } return st.nextToken(); } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ return Integer.parseInt(next()); } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ return Double.parseDouble(next()); } public long nextLong () throws IOException{ return Long.parseLong(next()); } } class Read { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer (br); int s; public String next () throws IOException { s = st.nextToken(); return st.sval; } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return (int ) st.nval; } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return st.nval; } }
六度空间 import java.io.*;import java.math.*;import java.util.*;public class Main { static InputReader ir = new InputReader (System.in); static Read in = new Read (); static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (System.out))); public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException{ solve(); out.flush(); } static List<Integer>[] g; static int n; public static void solve () throws IOException{ n = in.nextInt(); int m = in.nextInt(); g = new List [n + 1 ]; Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList <>()); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int u = in.nextInt(); int v = in.nextInt(); g[u].add(v); g[v].add(u); } double [] ans = new double [n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { ans[i] = 100.0 * bfs(i) / n; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { out.printf("%d: %.2f" , i, ans[i]); out.println("%" ); } } public static int bfs (int e) { Queue<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque <>(); boolean [] vis = new boolean [n + 1 ]; q.offer(e); vis[e] = true ; int cnt = 1 , dis = 1 ; while (!q.isEmpty()) { int size = q.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { int x = q.poll(); for (int y : g[x]) { if (!vis[y]) { vis[y] = true ; cnt++; q.offer(y); } } } dis++; if (dis > 6 ) break ; } return cnt; } } class InputReader { private final static int buf_size = 65536 ; BufferedReader br; StringTokenizer st; public InputReader (InputStream in) { br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (in), buf_size); st = new StringTokenizer ("" ); } public String next () throws IOException { while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) { st = new StringTokenizer (br.readLine()); } return st.nextToken(); } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ return Integer.parseInt(next()); } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ return Double.parseDouble(next()); } public long nextLong () throws IOException{ return Long.parseLong(next()); } } class Read { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer (br); int s; public String next () throws IOException { s = st.nextToken(); return st.sval; } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return (int ) st.nval; } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return st.nval; } }
功夫传人 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define MAX 100005 int winners[MAX];main (){ vector<int >peoples[MAX]; int k, id, x, N; double r,Z, sum=0.0 ; cin >> N >> Z >> r; for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++){ cin >> k; for (int j = 0 ; j < k; j++){ cin >> id; peoples[i].push_back (id); } if (k == 0 ){ cin >> x; winners[i] = x; } } if (N==1 ){ cout << int (winners[0 ]*Z); return 0 ; } queue<int > q; q.push (0 ); int level=0 ; while (!q.empty ()) { int t=q.size (); level++; for (int i=0 ;i<t;i++) { int top=q.front (); q.pop (); for (int j=0 ;j<peoples[top].size ();j++) { q.push (peoples[top][j]); double temp=Z*winners[peoples[top][j]]*pow (1 -r*0.01 ,level); sum+=temp; } } } cout << int (sum); }
列出连通集 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define CLOSE 0 void DFS (int vertex) ;void BFS (int vertex) ;int getNext (int y,int x) ;int getInsideNext (int y) ;int matrix[12 ][12 ];int isVisited[12 ]={0 };int n;int main () { int e; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&e); for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++){ for (int j=0 ; j<n; j++){ matrix[i][j]=CLOSE; } } int y,x; for (int i=0 ; i<e; i++){ scanf ("%d%d" ,&y,&x); matrix[y][x]=1 ; matrix[x][y]=1 ; } for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++){ if (!isVisited[i]){ printf ("{" ); DFS(i); int flag=1 ; for (int j=0 ; j<n; j++){ if (!isVisited[j]){ printf (" }\n" ); flag=0 ; break ; } } if (flag){ printf (" }\n" ); } } } for (int i=0 ; i<12 ; i++) isVisited[i]=0 ; for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++){ if (!isVisited[i]){ printf ("{" ); BFS(i); int flag=1 ; for (int j=0 ; j<n; j++){ if (!isVisited[j]){ printf (" }\n" ); flag=0 ; break ; } } if (flag){ printf (" }" ); } } } return 0 ; } int getInsideNext (int y) { for (int x=0 ; x<n; x++){ if (matrix[y][x]!=CLOSE){ return x; } } return -1 ; } int getNext (int y,int x) { for (int i=x+1 ; i<n; i++) { if (matrix[y][i]!=CLOSE) { return i; } } return -1 ; } void DFS (int vertex) { printf (" %d" ,vertex); isVisited[vertex]=1 ; int w=getInsideNext(vertex); while (w!=-1 ){ if (!isVisited[w]){ DFS(w); } w=getNext(vertex,w); } } void BFS (int vertex) { if (!isVisited[vertex]) printf (" %d" ,vertex); isVisited[vertex]=1 ; int size=0 ; int da[12 ]={0 }; for (int x=0 ; x<n; x++){ if (matrix[vertex][x]!=CLOSE && !isVisited[x]){ printf (" %d" ,x); da[size++]=x; isVisited[x]=1 ; } } for (int i=0 ; i<size; i++){ BFS(da[i]); } }
哈利波特的考试 import java.io.*;import java.math.*;import java.util.*;public class Main { static InputReader ir = new InputReader (System.in); static Read in = new Read (); static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (System.out))); public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException{ int T = 1 ; while (T-- > 0 ) solve(); out.flush(); } static int n; static int [][] dis; static int INF = (int ) 1e9 ; public static void solve () throws IOException{ n = in.nextInt(); int m = in.nextInt(); dis = new int [n][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) Arrays.fill(dis[i], INF); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int u, v, w; u = in.nextInt() - 1 ; v = in.nextInt() - 1 ; w = in.nextInt(); dis[u][v] = dis[v][u] = w; dis[u][u] = dis[v][v] = 0 ; } floyd(); int pos = 0 , distance = INF; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int mx = 0 ; for (int j : dis[i]) { if (j != INF) mx = Math.max(mx, j); else { out.print(0 ); return ; } } if (mx < distance) { distance = mx; pos = i + 1 ; } } out.print(pos + " " + distance); } public static void floyd () { for (int k = 0 ; k < n; k++) { for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { dis[i][j] = Math.min(dis[i][j], dis[i][k] + dis[k][j]); } } } } } class InputReader { private final static int buf_size = 65536 ; BufferedReader br; StringTokenizer st; public InputReader (InputStream in) { br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (in), buf_size); st = new StringTokenizer ("" ); } public String next () throws IOException { while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) { st = new StringTokenizer (br.readLine()); } return st.nextToken(); } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ return Integer.parseInt(next()); } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ return Double.parseDouble(next()); } public long nextLong () throws IOException{ return Long.parseLong(next()); } } class Read { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer (br); int s; public String next () throws IOException { s = st.nextToken(); return st.sval; } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return (int ) st.nval; } }
装箱问题 import java.io.*;import java.math.*;import java.util.*;public class Main { static InputReader ir = new InputReader (System.in); static Read in = new Read (); static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (System.out))); public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException{ int T = 1 ; while (T-- > 0 ) solve(); out.flush(); } public static void solve () throws IOException{ int n = in.nextInt(); List<Integer> box = new ArrayList <>(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int v = in.nextInt(); int idx = -1 ; boolean f = false ; for (int j = 0 ; j < box.size(); j++) { if (box.get(j) >= v) { box.set(j, box.get(j) - v); idx = j + 1 ; f = true ; break ; } } if (!f) { box.add(100 - v); idx = box.size(); } out.println(v + " " + idx); } out.println(box.size()); } } class InputReader { private final static int buf_size = 65536 ; BufferedReader br; StringTokenizer st; public InputReader (InputStream in) { br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (in), buf_size); st = new StringTokenizer ("" ); } public String next () throws IOException { while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) { st = new StringTokenizer (br.readLine()); } return st.nextToken(); } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ return Integer.parseInt(next()); } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ return Double.parseDouble(next()); } public long nextLong () throws IOException{ return Long.parseLong(next()); } } class Read { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer (br); int s; public String next () throws IOException { s = st.nextToken(); return st.sval; } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return (int ) st.nval; } }
月饼 import java.io.*;import java.math.*;import java.util.*;public class Main { static InputReader ir = new InputReader (System.in); static Read in = new Read (); static Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter (new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (System.out))); public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException{ int T = 1 ; while (T-- > 0 )solve(); out.flush(); } public static void solve () throws IOException { int n = in.nextInt(); double D = in.nextInt(); mk[] cake = new mk [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { cake[i] = new mk (); cake[i].storage = in.nextDouble(); } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { cake[i].sale = in.nextDouble(); cake[i].unit_price = cake[i].sale / cake[i].storage; } Arrays.sort(cake, new Comparator <mk>() { @Override public int compare (mk a, mk b) { if (a.unit_price < b.unit_price) { return 1 ; } if (a.unit_price > b.unit_price) { return -1 ; } return 0 ; } }); double sum = 0 ; for (mk i : cake) { if (i.storage < D) { D -= i.storage; sum += i.sale; }else { sum += D * i.unit_price; break ; } } out.printf("%.2f" , sum); } } class mk { double storage, sale; double unit_price; } class InputReader { private final static int buf_size = 65536 ; BufferedReader br; StringTokenizer st; public InputReader (InputStream in) { br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (in), buf_size); st = new StringTokenizer ("" ); } public String next () throws IOException { while (!st.hasMoreTokens()) { st = new StringTokenizer (br.readLine()); } return st.nextToken(); } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ return Integer.parseInt(next()); } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ return Double.parseDouble(next()); } public long nextLong () throws IOException{ return Long.parseLong(next()); } } class Read { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in)); StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer (br); int s; public String next () throws IOException { s = st.nextToken(); return st.sval; } public String nextLine () throws IOException{ return br.readLine(); } public int nextInt () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return (int ) st.nval; } public double nextDouble () throws IOException{ s = st.nextToken(); return st.nval; } }
主观题 一笔画 public static void solve () throws IOException{ int n = in.nextInt(); int m = in.nextInt(); int [] deg = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int x = in.nextInt() - 1 ; int y = in.nextInt() - 1 ; deg[x]++; deg[y]++; } int cnt = 0 ; for (int i : deg) if ((i & 1 ) == 1 ) cnt++; out.print(cnt == 0 || cnt == 2 ? "Y" : "N" ); }